News
Why employees forget 90% of training within a week (and what to do about it)
Why employees forget 90% of training within a week (and what to do about it)
In a training context, the forgetting curve shows that learners will forget an average of 90% of what they have learned within the first seven days.
When it comes to forgetting, our brain’s imperfection does not affect only the information gathered at work. After all, don’t forget what article we read, what movie we saw, what conversation we overheard, or who we came across?
Forgetting work-related information, instructions, and responsibilities, however, results in inefficient time management and low productivity, which cost the employer a lot of money.
Why do people forget?
Forgetting is not only an issue of the modern age, troubled by the overload of information. Hermann Ebbinghaus, a German psychologist, pioneered memory and forgetting research before 1885.
The outcome of his tests and observations is the Forgetting Curve, which shows that we forget the majority of information after a few hours from their receipt. George Armitage Miller followed up on Ebbinghaus’s studies with a primary focus on short-term memory.
His work gave birth to the Magical Number Seven theory, i.e. the amount of information a human can hold in his or her short-term memory is 7 ± 2. Some people can hold 5 objects while others 7 or 9. This means that you want to remember a 10 digits phone number, account number or a long password, you need to pay more attention and spend more time.
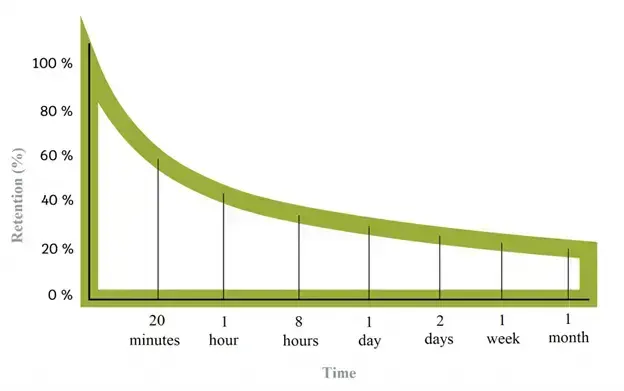
Hermann Ebbinghaus’ Forgetting Curve
The forgetting rate also depends on several external factors, such as stress, emotions, or physical and mental condition.
Forgetting has a positive side
The reason why information “vanish” is not negligence. Forgetting is closely connected to the survival instinct developed in humans a long time ago.
They say time is the best healer. However, it is the forgetting that eliminates things unrelated to human’s future path in this context. It is the forgetting which allows us to receive and store new information and knowledge.
Minimize the forgetting rate
There are no wonder memory pills to help you, but the experts didn’t forget this issue. They came up with many techniques and methods. In a nutshell, they all agree that long-term forgetting can be reduced by inner motivation, associations, and repeating.
The inner motivation could be our fondness of a specific topic or the benefit of the information, which helps us solve a current problem. Associate a new piece of information with a clue, and the probability of storing the information in the long-term memory increases. The crucial element for this step is associations.
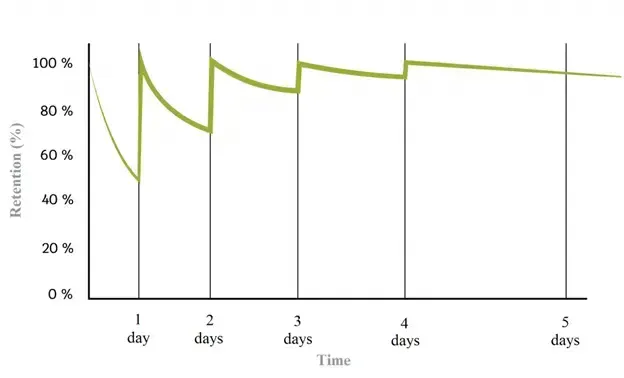
Curve indicating the information remembering rate by days of review.
Reviewing also boosts your memory. To maximize the effects, repeat information at specific time intervals. Memorizing large amounts of information in a short time, very well known from the long nights before tests, is meaningless in terms of long-time memory.
A popular method is the “2-7-12 rule,” which says that after the second review, we will remember the information for 2 days, after the third review for 7 days, and after the fourth for 12 days.
However, all of these are obsolete methods and techniques that can have the desired effect on employees reluctant to learn hundreds of pages with a small modification and smarter application.
More appropriate educational tools
There are specific staff training methods designed for the digital environment. These include as online courses (e-learning), instructional videos, gamification and digital onboarding—and it is the last of these continuing to grow in popularity among larger corporations.
The advantage of onboarding is that, besides your own employees, it can often also be rolled out with slight adjustments to educate your customers and partners too.
So, what exactly is onboarding? Digital onboarding is an educational process based on direct interaction with an app, software package, or information systems, such as SAP or Sage.
In the real world, an onboarding guide delivers relevant help at the right time. For instance, only when the user is new in the app as the guide knows the user has logged in for the first time or only when they become an advanced user who has been using the app for a month.
Digital onboarding can offer personalized help based on various input data, such as the employee’s attendance or previous experience with the app. All of the above is covered by our onboarding features that give you the option to create a similar guide for any of your business software.
If the employee is late on his or her tasks because the software is slowing him or her down while ignoring the context-sensitive help made possible by a digital adoption platform, it is not rocket science to determine who is responsible.
Article by
Daniel Gripton
Share this article





